active site of an enzyme
Answer 1 of 3. The active site of an enzyme is the region that.
 |
| Active Site Of An Enzyme Definition Mechanism Characteristics Role Biology Reader |
What happens when the active site of an enzyme is altered by changing pH or temperature.
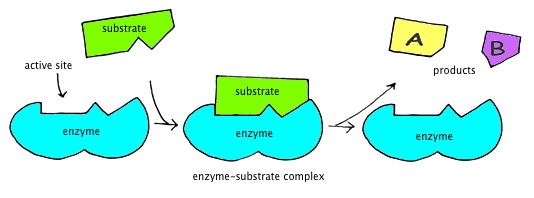
. The site of an enzyme where a catalytic reaction occurs when the enzyme and substrate specifically bind to each other. Enzymes have active sites to bind to the substrate enzyme-substrate complex forming products by allowing the formation of bonds between the substrates. 1 of 16 Active site of an enzyme May. 14 2020 5 likes 1180 views Education The active site takes the form of a cleft or pocket which is formed by groups that come from different parts of.
Cis involved in the catalytic. A region on an enzyme. Abinds a noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzyme. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions in cells.
Some enzymes have to be activated in order to work. Enzyme active sites achieve TS stabilization by forming critical interactions with substrate s. In biology the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules.
Feature of the active site The active site is a three-dimensional cleft formed by groups that come from different parts of the amino acid sequence The active site takes up a. Active sites are important because they are responsible for the catalytic activity of. The active site is formed by the contribution of amino acid residues specific positions. While in some a.
The discovery was made in a version of the. The active site is a groove or pocket. Active Site Definition. Scientists have now uncovered the 3-D structure of the enzymes chemically active site which belongs to a novel protein family.
Bis inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor. Is identical to that of any other enzyme. The active site consists of residues that form temporary. Methods in Enzymology 2016 View all Topics Download as PDF.
Higher temperatures disrupt the shape of the active site which will reduce its. The active site of an enzyme a. The active site of an enzyme is the region that binds the substrates and cofactor if any The interaction of the enzyme and substrate at the active site promotes the formation of the. In the lock and key hypothesis the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules.
Solution Verified by Toppr The active site is the region of the enzyme where substrate molecule bind and undergo a chemical reaction. ACTIVE SITE AND ES COMPLEX. Is the part of the enzyme where the substrate can fit. Enzyme Active Site Enzyme active sites achieve TS stabilization by forming critical interactions with substrate s.
Location where S binds during chem reaction 3-D crevice like formed by secondary and tertiary structures of protein part of enzyme binding. Features that Determine Active Site Specificity. The place where these molecules fit is called the active site. Is destroyed during a.
The active site possesses amino acid residues that participate in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme. Activators are effectors that bind to an. The AA can be the same or different from the ones used in substrate binding. What is active site of enzyme in biology.
Methods in Enzymology 2016 Download as PDF About this page Repair of Double. Here we explore recently reported computational chemistry-based methods for the prediction of active amino acids in protein 3D structures including biochemically important distal residues. This is crucial for the enzymes.
 |
| Active Site Of An Enzyme Definition Mechanism Characteristics Role Biology Reader |
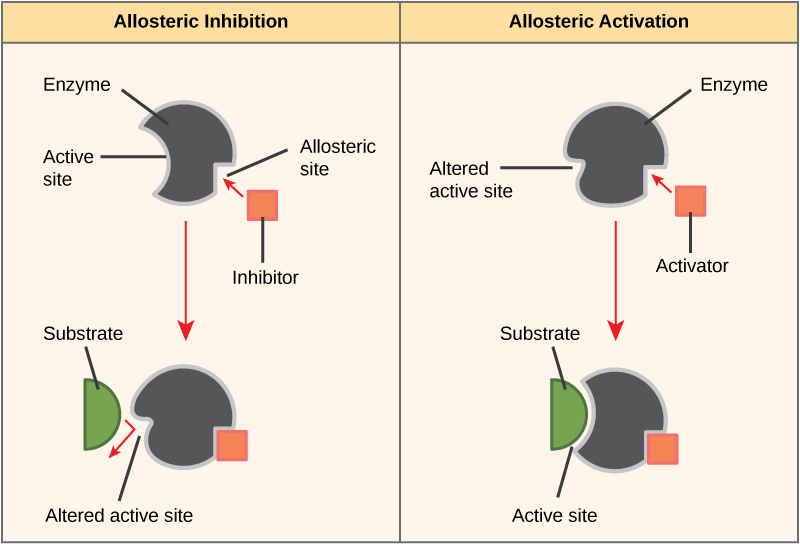 |
| What Is The Difference Between Allosteric Site And Active Site Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms |
 |
| Bits And Bytes Of Biology What Is Active Site Of An Enzyme |
 |
| Enzymes Function Definition And Examples |
 |
| 6 10 Enzymes Chemistry Libretexts |
Posting Komentar untuk "active site of an enzyme"